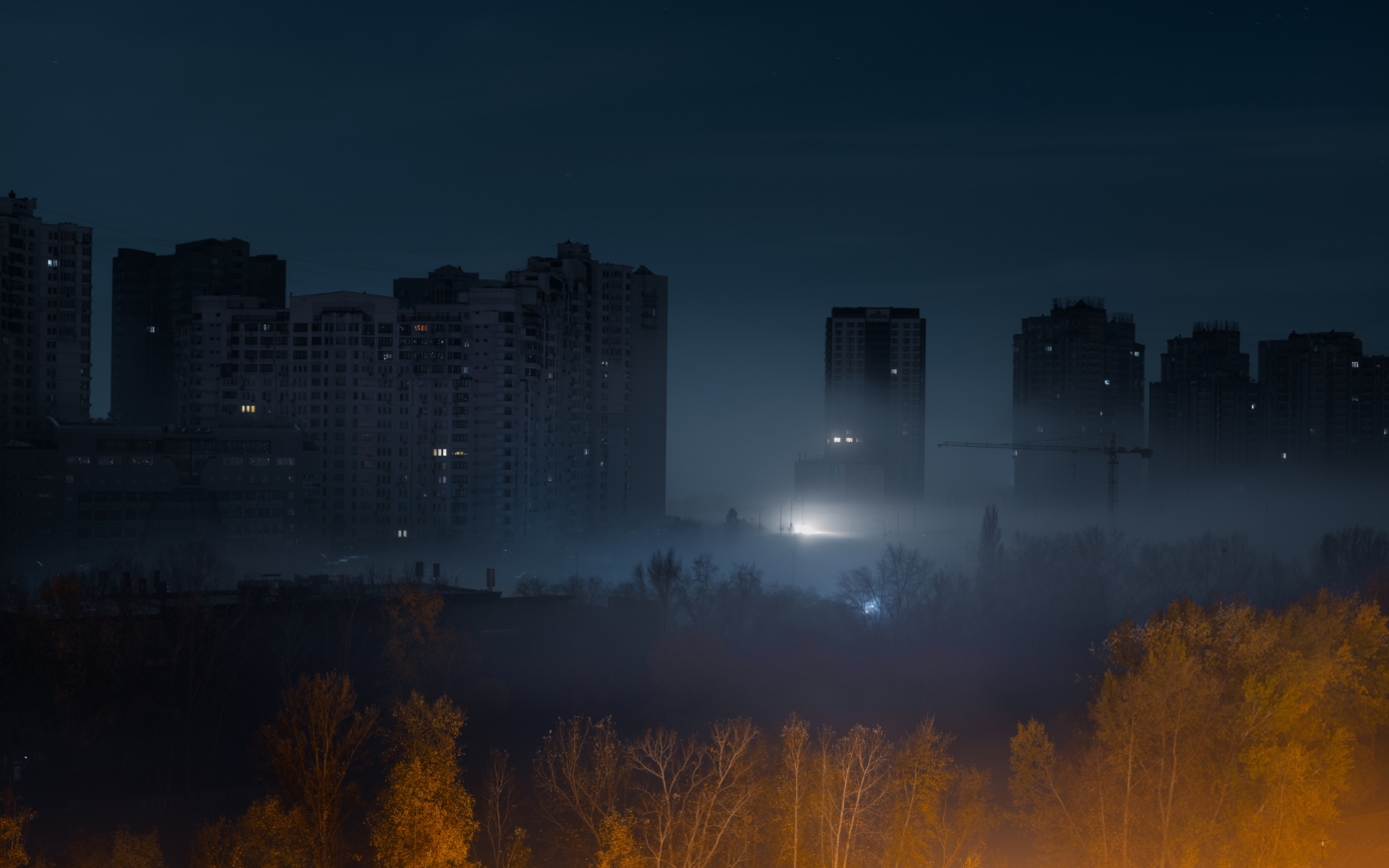
The potential of the night
Once a sanctuary for dreams and imagination, nighttime has now been relegated to the mere role of a utilitarian prelude to daytime. Nocturnal realms possess an alchemical power capable of transfiguring our perceptions. However, when viewed through the lens of urban uses, the night also exacerbates inequalities and raises questions about the possibility of achieving an urban night that is accessible to everyone. Exploring the range of possibilities associated with the night reveals it as a space-time where complex interactions are woven that could be revitalized through a chronotopic and inclusive architecture.